Java File
我们先来比较 IO 和 NIO 两种写入文件的实现:
- 使用 IO 实现:
public void copyFile(File source, File dest) throws IOException {
try(InputStream in = new FileInputStream(source);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dest);) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int length;
while((length = is.read(buffer)) >0) {
os.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
}
}
- 利用 NIO 实现:
public void copyFile(File source, File dest) throws IOException {
try(FileChannel inChannel = new FileInputStream(source).getChannel());
FileChannel outChannel = new FileOutputStream(dest).getChannel();) {
for (long count = inChannel.size; count >0; ) {
long transferred = inChannel.transferTo(inChannel.position(), count, outChannel);
count -= transferred;
}
}
}
在面试时可能会问:
- 不同 copy 方式,底层实现机制有什么区别?
- 为什么零拷贝(zero-copy)可能有性能优势?
- Buffer 分类与使用
- Direct Buffer 对垃圾收集等方面的影响与实践选择。
用户态(User Space)和内核态(Kernel Space)
操作系统内核、硬件驱动等运行在内核态空间,具有相对高的特权 用户态空间,则是给普通应用和服务使用。
当我们使用输入输出流进行读写时,实际上进行了多次上下文切换,例如应用读取数据时,先在内核态将数据从磁盘读到内核缓存,再切换到用户态将数据从内核缓存读取到用户缓存。
而写入步骤正好相反,可以参考下图:
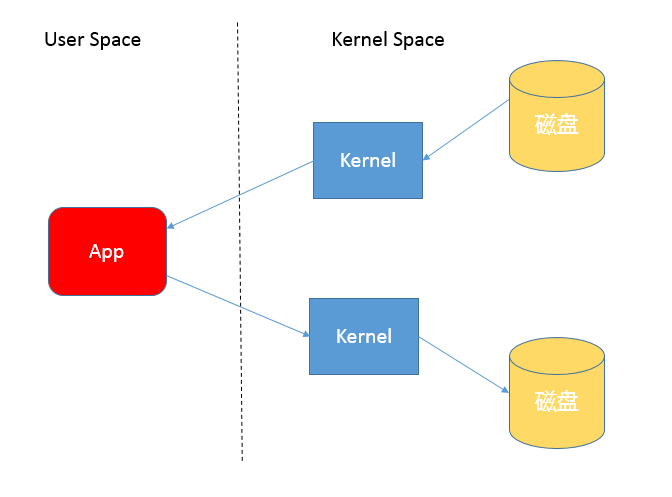
所以这种方式一定会带来额外的开销,可能降低 IO 的效率。
而基于 NIO transferTo 的实现方式,在 Linux 和 Unix 上,则会使用到零拷贝技术,数据传输并不需要用户态参与,省去了上下文切换的开销和不必要的内存拷贝,进而可能提高应用拷贝性能。注意,transferTo 不仅可以用于文件拷贝,还可以用于读取磁盘文件,然后进行 Socket 发送,同样可以享受这种机制带来的性能和扩展性提高。
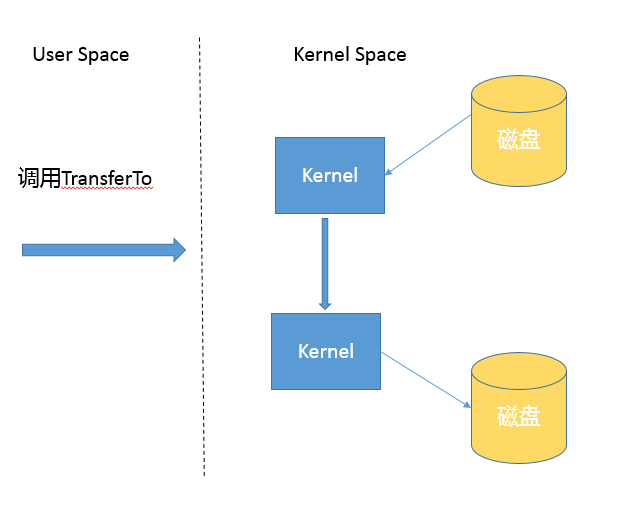
不同 copy 方式,底层实现机制有什么区别?
/**
* native 代码实现用户态空间拷贝
*/
public static Path copy(Path source, Path target, CopyOption... options) throw IOException {
FileSystemProvider provider = provider(source);
if (provider(target) == provider) {
// same provider
provider.copy(source, target, options);
} else {
// diff providers
CopyMoveHelper.copyToForeignTarget(source, target, options);
}
return target;
}
/**
* Stream 用户态读写
*/
public static Path copy(InputStream in, Path target, CopyOption... options) throw IOException
/**
* Stream 用户态读写
*/
public static Path copy(Path source, OutputStream out, CopyOption... options) throw IOException
提高 copy 操作 IO 性能有一些建议:
- 在程序中,使用缓存等机制,减少 IO 次数
- 使用 transferTo 等机制,减少上下文切换和额外 IO 操作
- 尽量减少不必要的转换过程,如编解码,对象序列化和反序列化,比如操作文本文件或者网络通信,如果不是过程中需要文本信息,可以考虑不要将二进制信息转换成字符串,直接传输二进制信息。
掌握 NIO Buffer
Buffer 是 NIO 操作数据的基本工具,Java 为每种原始数据都提供了相应的 Buffer 实现(bool除外),Dierct Buffer 在垃圾收集等方面的特殊性,需要重点掌握。
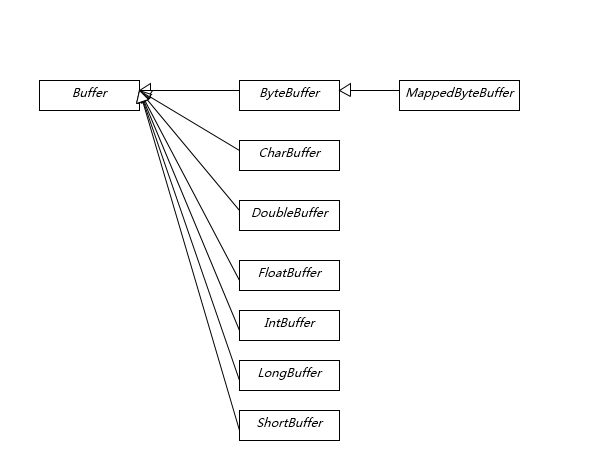
Buffer 有几个基本属性
- capacity 反映 Buffer 的大小,本质是数组的长度
- position 操作的数据起始位置
- limit 操作限额。在读取操作时,一般将 limit 设置为所容纳数据的上限;而写入操作时,则会设置容量或容量以下的可写限度。
- mark 记录上一次 position 的位置,默认是 0,optional。
Buffer 的4步基本操作
- Write data into Buffer
- Call buffer.flip()
- Read data out of the Buffer
- Call buffer.clear() or buffer.compat()
RandomAccessFile rFile = new RandomAccessFile("data/nio-data.txt", "rw");
FileChannel inChannel = rFile.getChannel();
// create buffer with capacity of 48 bytes
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
int bytesRead = inChannel.read(buffer);
while (bytesRead != -1) {
buffer.flip(); // make buffer ready for read
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println(buffer.getChar()); // read 1 byte at a time
}
buffer.clear(); // make buffer ready for writing
bytesRead = inChannel.read(buffer);
}
rFile.close();